PDF] Kinetics and Mechanism of the Food Dye FD&C Red 40 Adsorption
4.7 (347) · $ 10.50 · In stock
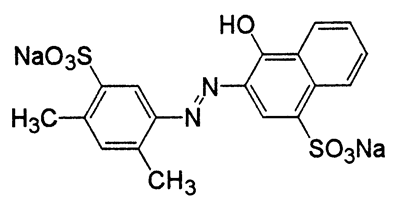
The kinetics and mechanism of the food dye disodium 6-hydroxy-5-((2-methoxy-5-methyl-4-sulfophenyl)azo)-2-naphthalenesulfonate (FD&C Red 40) adsorption onto chitosan were studied. The effects of pH (5.7 to 7.4), chitosan dosage [(250 to 500) mg·L–1], deacetylation degree (42 % to 84 %), and particle size [(0.10 to 0.26) mm] were investigated. The adsorption reaction models were used to evaluate the kinetic behavior. Infrared analysis and models based on mass transfer phenomena were used to investigate the adsorption mechanism. The maximum adsorption capacity (300 mg·g–1) was found at a pH 5.7, chitosan dosage of 250 mg·L–1, deacetylation degree of 84 %, and particle size of 0.10 mm. Pseudosecond-order and Elovich models were the most appropriate to fit the experimental data of adsorption kinetics. The adsorption process was controlled by intraparticle diffusion, film diffusion, or convection according to the experimental conditions. Infrared analysis showed the chemical interaction between chitosan and fo

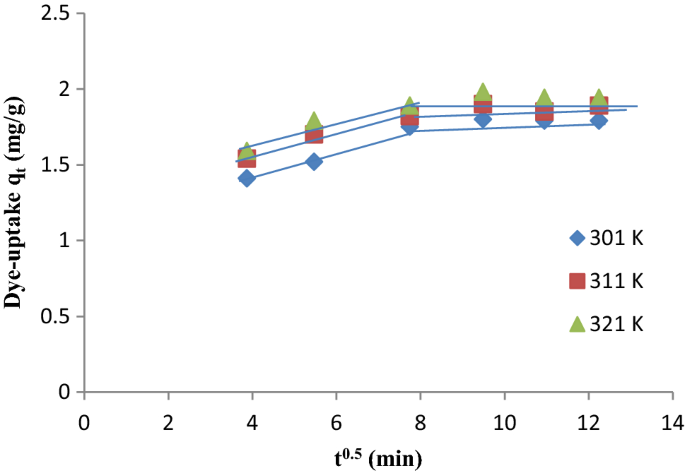
Adsorption kinetics fitted to the different models for FD&C Red 40

PDF] Removal of FD&C Red No.40 Food Dye from an Aqueous Solution
Kinetics and mechanisms of congo-red dye removal from aqueous

Adsorption of FD&C Red No. 40 by chitosan: Isotherms analysis

PDF) Dye Adsorption by Leather Waste: Mechanism Diffusion, Nature

Degradation products of the artificial azo dye, Allura red

PDF] Kinetics and Mechanism of the Food Dye FD&C Red 40 Adsorption

Use of Chitosan with Different Deacetylation Degrees for the

PDF] Removal of FD&C Red No.40 Food Dye from an Aqueous Solution

Two-stage optimization of Allura direct red dye removal by treated

PDF) Biosorption of food dyes onto Spirulina platensis
Frontiers Extraction, Analytical and Advanced Methods for
![PDF] Kinetics and Mechanism of the Food Dye FD&C Red 40 Adsorption](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/4af49f0f86df981087558721a73a321f677cd669/1-Figure1-1.png)